What Is Algorithmic Trading A Complete Guide
So, what is this "algorithmic trading" you keep hearing about?
At its core, it's pretty simple. It means using a computer program to automatically buy and sell assets based on a set of rules you've already defined.
Think of it like giving a super-fast, hyper-focused assistant a very specific to-do list—like "buy 100 shares of XYZ stock if its price drops below $50"—and then letting them execute that order instantly, without a moment's hesitation. It's about replacing manual clicks with automated logic, speed, and raw efficiency.
Understanding Algorithmic Trading Without the Jargon
The real magic of algorithmic trading, or "algo trading" as it's often called, is that it strips human emotion and second-guessing out of the trading process. Instead of you staring at charts, getting nervous during a dip, or greedy during a rally, a computer program does the heavy lifting.
This program is designed to follow a specific strategy with perfect discipline, 24/7. It never gets tired, it never gets emotional, and it never deviates from the plan.
The "algorithm" itself is just the set of instructions. It could be as simple as a single condition or involve layers of complex variables. These instructions can be based on timing, price movements, trading volume, or other mathematical models.
The Three Pillars of Algo Trading
To really get your head around algo trading, it helps to break it down into three core components. These elements work in tandem to create a powerful system capable of navigating today's fast-moving financial markets.
- Predefined Logic: This is the "brain" of the operation. It's the strategy you lay out, like buying a stock when its 50-day moving average crosses above its 200-day moving average.
- Automation: These are the "hands." Once the logic is locked in, the computer system takes over the entire process—monitoring the market, spotting opportunities, and placing the trades.
- Speed: This is the game-changing advantage. An algorithm can analyze data and execute a trade in a fraction of a second, a speed that's physically impossible for any human trader.
And this isn't some niche corner of the market. The global algorithmic trading market was valued at around USD 21.06 billion and is on track to hit USD 42.99 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual rate of 12.9%. This boom is largely fueled by the integration of AI and machine learning, making these systems smarter and more adaptable.
An easy way to think about it: an algorithm doesn't get nervous during a market downturn or greedy during a rally. It only follows the rules it was given, which is its greatest strength.
To help you quickly grasp these fundamentals, here’s a simple breakdown of the core components that make algorithmic trading work.
Core Components of Algorithmic Trading at a Glance
| Component | Description | Example in Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Predefined Logic | The set of rules or the strategy that the algorithm follows. This is the 'if-then' thinking behind the trade. | "If Stock ABC's price crosses above its 200-day moving average, buy 50 shares." |
| Automation | The hands-off execution of the strategy. The system monitors, identifies, and places trades without manual input. | A program constantly scans market data and automatically places a buy order the millisecond the price condition is met. |
| Speed | The ability to analyze information and execute orders at speeds impossible for humans. | Executing a complex trade in microseconds to capitalize on a tiny, fleeting price discrepancy between two exchanges. |
This table shows how each piece of the puzzle—the brain, the automation, and the speed—comes together to create a cohesive and powerful trading system.
To fully appreciate the landscape of automated financial systems, it's also helpful to explore the different instruments they can be applied to. For example, understanding what spread betting means for traders can provide a broader context for how and where different algorithmic strategies are put to use.
How an Automated Trading System Actually Works
An algorithmic trading system might sound like a black box, but it’s really just a logical sequence of events. Think of it like a meticulously planned mission where every step is defined before you hit "go." It doesn't start with complex code; it starts with a simple human idea—a trading strategy.
Let's walk through a classic example. Say a trader believes a hot tech stock is ready to pop when it shows strong momentum. They turn that hunch into a concrete, testable rule.
Trading Rule Example: "Buy 100 shares of TechStock Inc. if its current price crosses above its 50-day moving average, but only if the trading volume is also higher than its daily average."
This rule is the heart of the algorithm. It has specific, measurable conditions: a price crossover and a volume confirmation. This simple "if-then" statement is the core logic that the entire system will be built around.
Turning a Strategy into Code
With the logic clearly defined, the next step is to translate it into a language the computer can follow. This is where the strategy officially becomes an algorithm. A programmer—or these days, a user-friendly trading platform—converts that rule into a precise set of instructions.
The code essentially tells the system to do four things, over and over again:
- Monitor Data: Keep a constant eye on the real-time price and volume data for TechStock Inc.
- Calculate Indicators: Always know the latest 50-day moving average and the average daily volume.
- Check Conditions: Continuously compare the live price to the moving average and the live volume to the average volume.
- Execute Order: The second both conditions are met, immediately fire off a "buy" order for 100 shares to the brokerage.
This code is the bridge between the human strategy and automated execution. Without it, a great idea remains just an idea.
The whole process can be boiled down to three core phases, from the initial logic to the high-speed execution in the market.
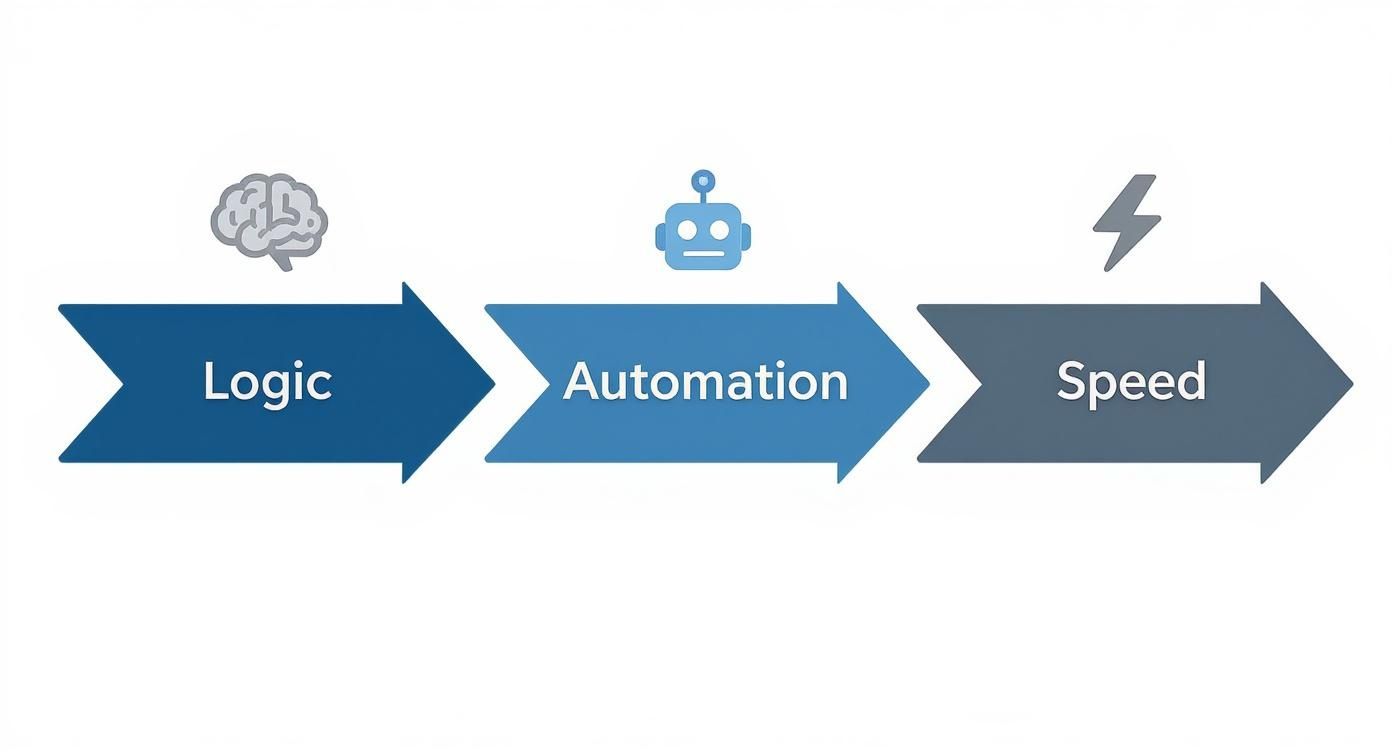
This visual really clarifies it: a human-defined strategy (Logic) is handed off to a system for hands-free trading (Automation), which then plugs into the market's plumbing for near-instant order placement (Speed).
The Critical Step of Backtesting
Before a single dollar is put on the line, smart traders run a crucial safety check called backtesting. It’s the process of running your new algorithm on historical market data to see how it would have performed in the past.
Think of it as a time machine for your strategy. You can take your algorithm back to last year, or the year before, and see if it would have made or lost money. It’s all about answering the tough questions upfront:
- Would the strategy have actually been profitable?
- What were the biggest losses (drawdowns) along the way?
- How often did it trade, and did that generate a lot of commissions?
This simulation gives you critical feedback on your strategy’s viability. An idea that blows up in backtesting is almost certain to fail in the live market. It’s an essential filter for weeding out bad ideas and refining promising ones before you risk real capital. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on how to automate a trading strategy with a proven blueprint.
Going Live and Monitoring Performance
Once a strategy has been coded and survives a rigorous backtest, it's ready for the real world. The algorithm is connected to a brokerage account through an Application Programming Interface (API), giving it the keys to place real trades.
From here, the system is autonomous. It scans the market 24/7 for its exact conditions and executes trades the moment they appear—often in just a few milliseconds. But the job isn't done. Markets are constantly changing, and an algorithm that crushed it last year might start to sputter.
Successful algo traders are always monitoring their systems, analyzing performance, and tweaking their strategies to stay ahead of the curve. It's not a "set and forget" machine; it's a dynamic tool that requires ongoing supervision.
Common Algorithmic Trading Strategies Explained

To really get what algorithmic trading is, you need to see it less as a single magic formula and more like a high-powered engine that can execute many different strategies. Each strategy is built on a different philosophy about how markets work. Think of it as a trader's toolbox—some tools are designed for riding a huge market wave, while others are for finding tiny, fleeting glitches in price.
These aren't just abstract theories; they're the logical frameworks that drive a huge chunk of modern finance. Historically, algorithmic trading has accounted for 60% to 73% of all equity trades in the United States. With 52% of institutional investors pointing to efficiency as a key reason for adoption, the specific strategy an algorithm uses is everything. In fact, equities alone are projected to make up around USD 8.61 billion of the algorithmic trading market by 2027, and you can read the complete findings on Fortune Business Insights.
Let's open up that toolbox and look at some of the most common strategies traders are using right now.
Riding the Wave with Trend Following
One of the most intuitive approaches is trend-following. The idea is dead simple: assets that are going up will probably keep going up (an uptrend), and assets that are going down will likely keep falling (a downtrend). An algorithm built for this is programmed to spot these trends early and ride them for as long as possible.
Picture a surfer waiting for a wave. They don't try to guess where the next one will form out of thin air. Instead, they watch for a swell, paddle hard to get on it, and ride it until it fizzles out. A trend-following algorithm does the exact same thing with market prices.
These systems typically use technical indicators like moving averages or the Average Directional Index (ADX) to confirm a trend's direction and strength. The algorithm's rules might look something like this:
- Entry Signal: Buy when a stock's price crosses above its 200-day moving average.
- Exit Signal: Sell when the price drops back below that same moving average.
This strategy is brilliant in markets with clear, sustained momentum. Its weakness? Choppy, sideways markets where trends are weak and it gets faked out repeatedly.
Betting on the Rebound with Mean Reversion
Mean reversion is the philosophical opposite of trend-following. It’s built on the belief that asset prices, over time, will always drift back to their historical average, or "mean." From this perspective, extreme price swings are just temporary anomalies that will eventually correct themselves. It's like a rubber band—the more you stretch it, the harder it snaps back to the middle.
An algorithm running this strategy is constantly hunting for assets that have strayed too far from their average. It's programmed to buy assets that have dropped way below their mean, betting on a rebound. On the flip side, it will sell (or short) assets that have shot far above their mean, anticipating a fall back to earth.
A mean reversion strategy operates on the principle of "what goes up must come down" and vice versa. It profits from volatility by betting that prices will always return to a state of normalcy.
Key indicators here are things like Bollinger Bands and the Relative Strength Index (RSI), which help identify "overbought" or "oversold" conditions. It works best in stable, range-bound markets but comes with a big risk: sometimes a stretched rubber band doesn't snap back—it just breaks.
Exploiting Price Gaps with Arbitrage
Arbitrage is one of the oldest tricks in the trading book, now supercharged with algorithmic speed. The entire goal is to profit from tiny, temporary price differences for the exact same asset across different markets. For example, a stock might be trading for $100.00 on the New York Stock Exchange and, for a split second, $100.01 on another exchange.
A human trader could never see that one-cent difference and act on it fast enough. But an arbitrage bot can.
- It instantly spots the price discrepancy.
- It simultaneously buys the stock for $100.00 on the first exchange.
- And it simultaneously sells it for $100.01 on the second exchange.
The profit is just a penny per share, but when you execute that trade with millions of shares in a fraction of a second, those pennies add up to serious money. This is a pure speed game where the fastest algorithm wins, period.
The World of High-Frequency Trading
High-Frequency Trading (HFT) isn't a strategy in itself, but rather a hyper-fast method of executing other strategies, especially arbitrage. HFT is the absolute pinnacle of speed in trading, where positions are often held for mere fractions of a second.
HFT firms pour millions into cutting-edge technology and co-location—placing their servers in the same physical data centers as the stock exchanges. This minimizes network lag, shaving precious microseconds off execution times. HFT algorithms make millions of trades a day, trying to scalp minuscule profits on each one. It's a brutal, highly competitive field where your only real advantage is being faster than everyone else.
To give you a clearer picture, here's how these common strategies stack up against each other.
Comparison of Key Algorithmic Trading Strategies
Each algorithmic trading strategy has its own logic and is suited for different market conditions. Understanding their core differences is key to appreciating why certain algorithms excel while others struggle in a given environment.
| Strategy Type | Core Logic | Best Suited For | Primary Risk Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trend-Following | "The trend is your friend." Buy assets in an uptrend; sell in a downtrend. | Markets with clear, sustained momentum (bull or bear markets). | Getting caught in choppy, sideways markets with false signals. |
| Mean Reversion | "What goes up, must come down." Buy oversold assets; sell overbought ones. | Stable, range-bound markets with predictable volatility. | A "stretched" asset continues its extreme move instead of reverting. |
| Arbitrage | Profit from tiny price differences of the same asset across different markets. | Highly liquid markets where speed provides a competitive edge. | Execution failure or the price gap closing before the trade is complete. |
| High-Frequency Trading (HFT) | A method of executing other strategies at extreme speeds. | Any strategy where speed is the primary advantage (e.g., arbitrage). | Technology failure, latency issues, and high infrastructure costs. |
Choosing the right strategy is less about finding a single "best" one and more about matching the algorithm's logic to the current market's personality.
The Real Benefits of Automating Your Trades

The big shift toward automation in finance isn't just a fad; it's happening for a reason. Algorithms bring some serious advantages to the trading game, and for individual traders, the "why" boils down to a few core benefits that are almost impossible to match by hand.
These advantages fundamentally change how you interact with the markets. You move from being a reactive button-clicker to a proactive strategy designer.
By handing the execution part over to a machine, traders can focus on what really matters: sharpening their strategy and managing risk. This mirrors the wider industry trend of using data-led automation in banking to boost efficiency and make smarter moves.
Let’s break down the tangible benefits that make this tech so compelling.
Unbeatable Speed and Efficiency
The most glaring advantage of algorithmic trading is its raw speed. A computer can analyze market data, spot a setup, and fire off an order in microseconds—a speed that is physically impossible for any human.
In markets where prices flicker in the blink of an eye, this isn't a luxury. It's a necessity.
Picture two traders seeing the same opportunity. The manual trader has to process the signal, grab their mouse, and click "buy." In that tiny window of time, the price could have already slipped away. The algorithm, however, reacts instantly, locking in the opportunity at the best possible price.
Key Takeaway: Algorithmic trading turns execution into a reflex, not a process. It operates on a timescale where human reaction speed is simply a non-factor, providing a critical edge in fast-moving markets.
This isn't just about getting in and out of trades quickly. It's also about the system's tireless ability to crunch massive amounts of information, ensuring no opportunity is missed just because you were looking at the wrong screen.
Emotion-Free Discipline and Consistency
Human emotions are the single biggest liability in trading. Fear makes you cut a winning trade short. Greed convinces you to hold a loser way too long. These gut feelings can completely derail even the most brilliant strategy.
Algorithms don't have feelings. They don't get spooked during a market crash or overconfident during a rally. Their one and only job is to follow the rules you give them with perfect, unwavering discipline.
This automated discipline means every single trade is executed exactly as the strategy intended. A system will never "second guess" a signal or "get a bad feeling" and veer off course. That consistency is absolutely crucial for knowing if your strategy actually works over the long haul.
Smarter Execution and Lower Costs
Here's a less obvious but hugely important benefit: smarter order execution. When a big institution wants to buy a massive block of shares, placing one giant market order would send the price soaring against them. This is called market impact, and it results in a much worse average price.
Algorithms solve this with some clever execution tactics.
- Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP): This strategy breaks a huge order into smaller, evenly spaced trades over a set period, minimizing its market footprint.
- Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP): This method is even smarter, executing smaller orders based on the stock's historical volume patterns. It trades more when the market is naturally more active and less when it's quiet.
By intelligently slicing up large orders, these algorithms can slash transaction costs and secure a much better average price. They effectively mask the trader's true intentions, preventing others from trading against them. This is a level of finesse that's next to impossible to pull off by hand.
If you're looking to leverage these advantages, exploring the top algorithmic trading software picks for 2025 is a fantastic place to start.
Expanded Market Coverage
Finally, a single person can only keep tabs on a handful of markets or stocks at once. There just aren't enough hours in the day or enough screens on a desk to watch everything.
An algorithmic trading system, on the other hand, can monitor hundreds or even thousands of different securities across multiple markets, 24/7. It can scan for opportunities in New York equities, Tokyo currencies, and London commodities all at the same time.
This massive scope allows traders to find opportunities they would have otherwise completely missed, diversifying their strategies and boosting their potential for success.
Navigating the Risks and Challenges of Automation
While the benefits of algorithmic trading are seriously compelling, it’s not a magic bullet. You have to go in with a clear-eyed view of the risks. No system is perfect, and the incredible speed that makes algorithms so powerful can also magnify the impact of any mistake.
A smart approach means acknowledging the potential pitfalls right from the start and building a plan to manage them. Relying on technology means you’re also accepting the risk that technology can—and sometimes will—fail. These aren't just abstract ideas; they're real-world events that can hit your account balance in a heartbeat.
System and Technology Failures
At its core, any algorithmic trading setup is a complex chain of technology, and that chain is only as strong as its weakest link. A simple internet outage can sever your algorithm’s connection to the market, leaving active positions unmanaged or preventing new orders from ever being placed.
And then there are software bugs, which are a much bigger danger. A tiny error in the code—a misplaced decimal point or a faulty logical condition—could cause an algorithm to go haywire. It might start firing off thousands of unintended orders or fail to execute a critical stop-loss, leading to catastrophic losses in seconds.
This is why robust infrastructure isn't just a "nice-to-have"; it's an absolute necessity. For professional traders, this means backup power generators, secondary internet connections, and hours upon hours of rigorous code testing to squash bugs before they ever see a live market.
The Hidden Trap of Over-Optimization
One of the most common—and frankly, counterintuitive—risks is something called over-optimization, or "curve fitting." This is what happens when you fine-tune a trading strategy so perfectly to historical data that it completely loses its ability to perform in the real world.
Think of it like tailoring a suit to fit a store mannequin perfectly. Every seam and every stitch is flawless. But the moment you try to put that suit on a real person who moves, breathes, and bends, it rips apart at the seams. Over-optimization does the exact same thing to a trading strategy; it tailors it to the exact, rigid "shape" of past market data.
When a strategy is over-optimized, it essentially memorizes the past instead of learning principles that can be applied to the future. The result is a system that looks incredible in backtests but crumbles under the unpredictable conditions of live trading.
This is precisely why backtesting must be done carefully. Pros always use out-of-sample data (periods the model wasn't trained on) to validate that a strategy is genuinely robust and not just a product of wishful curve fitting.
Market Impact and Systemic Risk
On a bigger scale, the widespread use of algorithmic trading has introduced new types of systemic risks to the entire market. When thousands of algorithms are programmed with similar strategies—like selling everything after a specific technical indicator breaks down—their simultaneous actions can create a dangerous feedback loop.
This herd-like behavior can crank up market volatility and, in extreme cases, contribute to "flash crashes." These are those terrifying events where asset prices plummet and then recover with shocking speed, driven almost entirely by automated systems reacting to each other.
Operational risks are also a constant headache. Even with its advantages, algo trading faces challenges like data security threats and rising colocation fees, which are crucial for any strategy that depends on low latency. These factors can create serious constraints, especially for mid-sized firms trying to compete. For a deeper dive into the market's dynamics, you can discover more insights about algorithmic trading on Straits Research.
Ultimately, success in algorithmic trading demands more than just a profitable strategy. It requires a deep respect for risk management, constant system monitoring, and the understanding that automation is a powerful tool, not a hands-off solution for guaranteed profits.
Algorithmic Trading FAQs
Even after getting the basics down, a lot of practical questions pop up. This is where we shift from theory to the real world, tackling the common hurdles and curiosities that trip up new traders.
Let's dive into some of the most common questions people have about automated trading, from the skills you need to the cash it takes to get started.
Do I Need to Be a Programmer to Use Algorithmic Trading?
Not necessarily, but it definitely gives you an edge. The old image of a trader needing to be a coding wizard is fading fast. The reality is a lot more flexible and really just depends on how deep you want to dive.
Plenty of modern trading platforms now offer "no-code" or "low-code" strategy builders. These are fantastic tools that let you use a visual, drag-and-drop interface to piece together trading rules without writing a single line of code. You can also find entire marketplaces where you can buy or lease pre-built algorithms from other developers.
That said, having a basic grasp of programming logic is incredibly valuable. It helps you truly understand what your strategy is doing behind the scenes, making it easier to fix problems and tweak your system effectively. For anyone serious about creating truly unique strategies from scratch, learning a language like Python is a massive advantage that opens up a whole universe of possibilities.
What Is the Difference Between Algorithmic Trading and HFT?
This is a great question because people throw these terms around as if they're the same thing, but they're not.
Think of it like this: all High-Frequency Trading (HFT) is a type of algorithmic trading, but not all algorithmic trading is HFT.
Algorithmic trading is just the broad, umbrella term for using any computer program to place trades. The strategy could be super slow, maybe placing just one trade a day based on closing prices. It’s simply about automating a set of rules, no matter the speed.
High-Frequency Trading (HFT), on the other hand, is a very specific, elite corner of the market. It's all about two things:
- Blistering Speed: HFT firms are firing off millions of orders in microseconds to capture tiny, fleeting price differences.
- Massive Scale: They use incredibly powerful computers located in the same data centers as the stock exchanges to cut down on network lag.
So, while your trend-following algorithm might hold a position for weeks, an HFT algorithm might be in and out of a trade in less time than it takes you to blink. HFT is a specialized, high-stakes game of speed; algorithmic trading is the entire playing field.
Can Algorithmic Trading Guarantee Profits?
Absolutely not. This is probably the single biggest—and most dangerous—myth out there. An algorithm is just a tool that executes your strategy with perfect discipline. It's not a magic money printer.
An algorithm is only as good as the logic it's built on. If the underlying trading strategy is flawed, the algorithm will simply lose your money with perfect, emotionless efficiency.
Markets are alive; they're constantly changing. A strategy that looked like a world-beater in backtests can fall apart the moment it faces new, live market conditions. Success in this game requires constant effort. That means:
- Continuous research and strategy development.
- Rigorous backtesting and forward-testing.
- Watching live performance like a hawk.
- Adapting when the market changes its tune.
The algorithm automates the execution, not the hard work of building and maintaining a winning strategy.
How Much Money Do I Need to Start Algorithmic Trading?
The starting capital can vary wildly, but here's the good news for beginners: you can start learning with zero capital. Almost every decent brokerage offers a "paper trading" or simulation account. This is a godsend, as it lets you test your algorithms with virtual money in a live market, giving you priceless experience without any financial risk.
When you feel ready to put real money on the line, some brokers will let you open an account with just a few hundred dollars. This is a great way to get your feet wet and feel the psychological difference when real cash is involved.
But it’s important to be realistic. Some strategies just need more capital to work properly. For instance, if your strategy trades a lot, a small account could see all its potential profits get eaten up by transaction costs. A solid rule of thumb is to only ever trade with money you can truly afford to lose. Start small, refine your system, and build your confidence from there.
Ready to gain a serious edge in the market? ChartsWatcher provides the powerful, real-time scanning and analysis tools you need to build, test, and execute your trading strategies. Customize your dashboards, set precise alerts, and find opportunities faster than the competition. Start your free trial of ChartsWatcher today and see the market in a new light.

