8 Proven Market Scanning Techniques for 2025
Unlocking Market Insights: Your 2025 Guide
In today's financial markets, success requires more than intuition and historical data. Proactive market scanning is essential for survival and growth. Understanding macroeconomic forces, competitive landscapes, and using digital intelligence and predictive analytics are crucial for strategic decisions.
Market analysis has evolved from basic observation to sophisticated, data-driven methods. Early reliance on fundamental metrics and industry reports has shifted with the rise of the internet and social media. Effective market scanning now demands a multifaceted approach, combining traditional methods and modern digital tools. This helps analysts and investors spot subtle changes in consumer behavior, technology, and regulations.
Effective Market Scanning in 2025
What defines effective market scanning in 2025? It's the ability to identify current trends and predict future ones. This means understanding how various market factors interact, including geopolitics, economic indicators, technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences. Just as Porter's Five Forces model transformed competitive analysis, today's market demands a new level of sophistication to match the digital age's speed and complexity.
This 2025 guide provides eight powerful market scanning techniques for professional traders, stock market analysts, financial institutions, independent investors, stock trading educators, and anyone using stock scanners and screeners. Mastering these strategies will help you identify emerging opportunities, mitigate potential risks, and make more informed investment decisions.
Eight Key Techniques
- Technique 1: Analyzing Social Media Sentiment
- Technique 2: Tracking Alternative Data Sources
- Technique 3: Utilizing Predictive Analytics
- Technique 4: Monitoring Regulatory Changes
- Technique 5: Assessing Global Economic Indicators
- Technique 6: Understanding Technological Disruptions
- Technique 7: Evaluating Competitive Landscapes
- Technique 8: Applying Behavioral Economics Principles
By implementing these techniques, you can position yourself for success in the evolving world of finance and day trading. This guide will empower you to navigate the complexities of the market and achieve your financial goals.
1. PESTEL Analysis
PESTEL analysis, which stands for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal, is a cornerstone of market scanning for professional traders, analysts, and investors. It provides a structured framework for understanding the macro-environmental factors that influence market dynamics and individual asset performance. By systematically examining these external forces, you can better anticipate market shifts, identify emerging opportunities, and manage potential risks. This makes PESTEL analysis a crucial tool for anyone involved in financial markets.
Understanding the Six Dimensions
-
Political: This dimension encompasses government policies, political stability, regulations, and trade agreements. These factors can significantly impact specific industries and overall market sentiment. A change in trade policy, for instance, could drastically affect businesses involved in importing and exporting. Political instability in a particular region might also pose investment risks.
-
Economic: Economic factors include interest rates, inflation, GDP growth, unemployment rates, and exchange rates. These macroeconomic indicators influence consumer spending, investment decisions, and overall market performance. Keeping an eye on these indicators is essential for understanding market trends.
-
Social: Social factors involve cultural trends, demographics, consumer behavior, and lifestyle changes. Identifying social shifts allows investors to anticipate demand for certain products or services. For example, the growing trend of sustainable living has significantly influenced investment in renewable energy companies.
-
Technological: This dimension includes technological advancements, innovation, automation, and research & development. Analyzing technological trends helps identify disruptive technologies that can reshape industries and create new investment opportunities. The rise of e-commerce, for instance, dramatically impacted retail businesses.
-
Environmental: Environmental factors include climate change, resource scarcity, pollution, and sustainability regulations. Growing environmental awareness and stricter regulations are driving investments in green technologies and impacting industries with significant environmental footprints.
-
Legal: This dimension considers labor laws, consumer protection laws, antitrust regulations, and intellectual property rights. These legal frameworks shape business practices and investment decisions, requiring businesses to adapt and comply.
Features and Benefits
The six-dimensional approach of PESTEL analysis offers a holistic view of the market environment, identifying both opportunities and threats that might not be apparent through other analytical methods. Its structured nature facilitates systematic data gathering and analysis. Its forward-looking perspective helps identify emerging trends before they become mainstream. The PESTEL framework is adaptable across various industries and can be applied at local, national, or global scales.
Real-World Applications
-
Netflix: Netflix capitalized on increasing internet speeds and evolving social preferences for on-demand entertainment (Technological & Social factors) to disrupt the traditional media industry.
-
Tesla: Tesla monitored environmental regulations and growing consumer concern for sustainability (Environmental & Social factors) to predict and capitalize on the electric vehicle market growth.
-
McDonald's: McDonald's adapts its menu based on evolving social trends toward healthier eating and local cultural preferences (Social factor) to maintain market relevance.
Pros and Cons
Pros: Holistic market view, early threat identification, improved strategic planning, encourages long-term vision, reveals hidden opportunities.
Cons: Resource intensive, requires continuous updates, potential information overload, difficulty translating findings into actionable strategies, dependent on data quality.
Tips for Effective Implementation
-
Focus: Prioritize the factors most relevant to your specific industry or investment strategy.
-
Weighting: Assign importance weights to different factors based on their potential impact.
-
Collaboration: Utilize cross-functional teams to gain diverse perspectives.
-
Regular Updates: Schedule regular PESTEL reviews (e.g., quarterly or bi-annually) to adapt to changing market conditions.
-
Strategic Integration: Directly link PESTEL findings to your investment strategies and portfolio management decisions.
By incorporating PESTEL analysis into your market scanning toolkit, you gain a powerful advantage in understanding market forces and making more informed investment decisions. It empowers you to look beyond short-term market fluctuations and anticipate long-term trends, ultimately leading to more robust and profitable outcomes.
2. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Porter's Five Forces Analysis is a powerful framework for understanding the competitive landscape of an industry. Developed by Michael E. Porter of Harvard Business School, this model helps traders, investors, and financial institutions analyze the forces shaping competition and profitability. Understanding these forces is crucial for making informed decisions about market entry, expansion, and overall portfolio strategy.
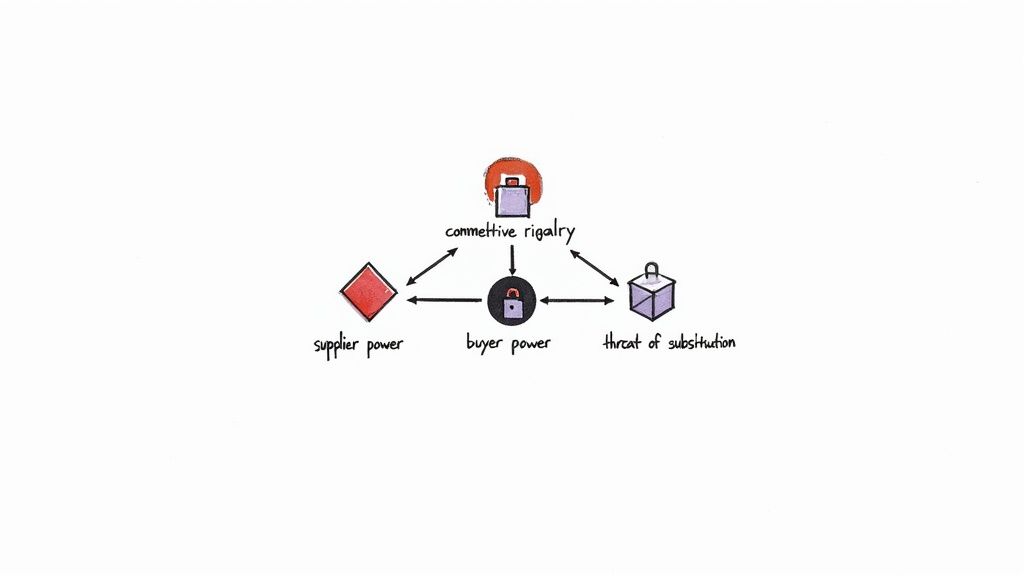
This model examines five key competitive forces:
- Competitive Rivalry: The intensity of competition among existing players. High rivalry often leads to price wars and reduced profitability.
- Supplier Power: The influence of suppliers to dictate prices and terms. Powerful suppliers can impact industry margins.
- Buyer Power: The influence of buyers to negotiate lower prices. Strong buyer power can also limit profitability.
- Threat of Substitution: The availability of alternative products or services that could meet the same customer need. High substitution threats can restrict prices and limit growth.
- Threat of New Entry: How easily new competitors can enter the market. Low barriers to entry increase competition and pressure existing businesses.
Why Porter's Five Forces Is Important
Porter's Five Forces offers a structured approach to industry analysis, going beyond simply analyzing current market share. It helps analysts understand the dynamics impacting profitability, identify potential threats and opportunities, and make more strategic investment decisions. It offers a focused analysis of the competitive dynamics within a specific industry.
Features and Benefits
- Industry-Specific Focus: Provides a detailed understanding of a specific industry's competitive dynamics.
- Profitability Focus: Directly addresses the factors influencing profitability.
- Structured Approach: Offers a systematic way to analyze competitive forces, promoting thoroughness.
- Identifies Threats and Opportunities: Highlights both direct and indirect competitive pressures, enabling proactive strategies.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Deep insights into competition
- Identification of potential threats
- Explanation of profitability differences
- Useful for market entry/exit decisions
- Helps develop competitive advantage strategies
Cons:
- Can be a static analysis, potentially missing rapid changes
- Less effective in volatile industries
- May not fully capture digital disruption’s impact
- Can oversimplify market interactions
- Focuses primarily on competition, not collaboration
Real-World Examples
- Amazon: Amazon likely used Porter's Five Forces to identify weaknesses in traditional retail, such as high fixed costs, allowing them to disrupt the industry.
- Apple: Apple likely analyzed the smartphone market using Porter's Five Forces. They recognized the opportunity to differentiate through design and user experience.
- Southwest Airlines: Southwest successfully identified an opportunity in the short-haul market by recognizing low buyer switching costs and the potential for cost leadership.
Tips for Implementation
- Be Specific: Apply the framework at a specific product or service level.
- Analyze Trends: Identify trends influencing each force.
- Quantify: Quantify the impact of each force using metrics like market share and price elasticity.
- Consider Digital Factors: Explicitly account for digital disruptions.
- Combine Approaches: Use Porter's Five Forces with other techniques like PESTLE and SWOT analysis.
Popularized By
Michael Porter, the Harvard Business Review, and strategy consulting firms like Boston Consulting Group (BCG) and Bain & Company have contributed to the widespread use of Porter's Five Forces.
By using Porter's Five Forces, traders and investors can gain a significant advantage. It provides a framework for in-depth analysis of the forces that shape industry competition and profitability.
3. Technology Scouting
Technology scouting is a crucial market scanning technique. Traders, analysts, and investors use it to gain an advantage. It's a systematic process. The goal is to identify emerging technologies and innovations. These innovations have the potential to disrupt markets. They can create new investment opportunities or threaten existing holdings.
By understanding how technology develops, you can anticipate shifts. These shifts might be in consumer behavior or industry dynamics. Ultimately, technology scouting helps predict changes in asset valuations. This proactive approach helps you stay ahead of the curve. You can capitalize on emerging trends before they become mainstream.
Technology scouting involves more than just reading headlines. It's a deep dive into scientific research, patent filings, and startup activity. It's about understanding broader technology trends. This multifaceted approach helps you identify potentially disruptive forces early on.
Consider some key questions. Are there new battery technologies poised to reshape the electric vehicle market? Could a new AI algorithm change financial modeling? Technology scouting helps answer these and other important questions.
Key Features and Benefits
Technology scouting offers several key advantages:
- Focus: It targets technological advancements that can move markets.
- Information Sources: It combines internal research with external data. This includes academic papers, industry reports, and venture capital activity.
- Proactive Approach: It identifies opportunities and threats before they impact market prices.
- Structured Process: It often uses dedicated teams or individuals with specialized expertise.
- Early Warning System: It provides insights into disruptive technologies. These can reshape industries and create new investment opportunities.
- Competitive Advantage: It allows for early adoption of new technologies. It also helps identify promising startups for potential investment.
Pros and Cons
Like any process, technology scouting has both advantages and disadvantages.
Pros:
- Early identification of disruptive technologies
- Pinpointing potential investment targets (e.g., startups, new sectors)
- Preventing technological obsolescence in portfolios
- Supporting informed research, development, and investment decisions
- Potential for first-mover advantage
Cons:
- Resource-intensive, requiring specialized knowledge and tools
- Difficulty in evaluating the potential of early-stage technologies
- Potential for information overload without proper filtering
- Risk of focusing on technologies that never achieve commercial success
- Requires effective knowledge transfer and integration into investment strategies
Real-World Examples
Several corporations utilize technology scouting successfully. IBM's horizon scanning program helps identify potential AI applications. This informs their strategic investments across various sectors. Procter & Gamble's Connect + Develop program uses external innovation to accelerate product development. It provides insights into emerging consumer trends. These companies demonstrate the value of seeking external technological advancements. This benefits both corporate strategy and investment decisions. Investors can apply similar principles to identify promising startups and sectors. This can ultimately help generate alpha.
Tips for Implementation
Want to get started with technology scouting? Consider these tips:
- Define Clear Criteria: Establish specific criteria for technology relevance to your investment strategy. Focus on your target sectors and the technologies that align with your investment thesis.
- Combine Automation and Expertise: Use automated scanning tools and data analytics platforms. But also retain human expertise for interpretation and analysis.
- Network Strategically: Connect with universities, research centers, and venture capital firms. This can provide access to cutting-edge research and emerging technologies.
- Develop an Evaluation Process: Create a systematic process for evaluating the potential market impact of identified technologies. Consider factors like market size, adoption rate, and the competitive landscape.
- Integrate with Investment Strategy: Regularly review findings with your investment team. Integrate technology insights into portfolio construction and risk management.
Evolution and Popularization
The concept of technology scouting became prominent with the rise of open innovation. Henry Chesbrough championed this concept. Publications like the MIT Technology Review helped popularize the practice. So did corporate innovation units like Google X and corporate venture capital arms like Intel Capital. Today, technology scouting is an essential element of market scanning. It is particularly valuable for those seeking to understand technological innovation.
Technology scouting belongs on this list. It provides a crucial perspective for understanding the future of markets. By identifying and evaluating emerging technologies, investors can make more informed decisions, mitigate risks, and find hidden opportunities. In a world of rapid technological change, technology scouting is a necessity.
4. Competitive Intelligence Gathering
Competitive Intelligence Gathering is more than just knowing your rivals. It's a powerful market scanning technique that involves systematically collecting, analyzing, and using information about competitors, customers, and market dynamics. This knowledge helps businesses and investors make smart decisions, anticipate competitor strategies, and spot potential market shifts. For traders and investors, understanding the competitive landscape is key to making sound investment choices.
This isn't a one-time task, but an ongoing process. It involves combining multiple data sources. These include public information like financial reports and news articles, proprietary data like customer surveys, and field intelligence gathered through industry events and networking. The focus is on both current and future competitor activities, encompassing both tactical and strategic intelligence. Critically, it also includes customer feedback about competitors, providing a valuable outside perspective.
Features of Effective Competitive Intelligence Gathering
Effective competitive intelligence gathering involves several key features:
-
Multi-Source Data Integration: Combining public records, proprietary research, and on-the-ground insights creates a complete picture.
-
Continuous Monitoring: The market is constantly changing. Consistent monitoring keeps you ahead of the curve.
-
Predictive Focus: Analyzing trends and anticipating future competitor actions allows for proactive strategies.
-
Tactical & Strategic Insights: From short-term pricing changes to long-term market positioning, competitive intelligence informs decisions at all levels.
-
Customer-Centric Perspective: Understanding customer perceptions of competitors offers invaluable context.
Real-World Examples
Real-world examples demonstrate the importance of competitive intelligence:
- Coca-Cola and PepsiCo constantly track each other’s marketing campaigns and product launches.
- Samsung closely monitors Apple’s product development.
- Pharmaceutical companies follow their competitors' clinical trial registries.
- Airlines frequently adjust pricing based on competitor fares.
These examples highlight the broad use and significance of competitive intelligence across various industries.
Advantages of Competitive Intelligence
Competitive intelligence provides several key benefits:
-
Direct Insights: Understand competitor strengths, weaknesses, strategies, and capabilities.
-
Opportunity Identification: Uncover market gaps and potential areas for growth and innovation.
-
Informed Decision-Making: Make data-driven decisions regarding pricing, product development, and market positioning.
-
Reduced Risk: Anticipate and mitigate potential threats, avoiding unexpected challenges.
-
Performance Benchmarking: Compare your performance to competitors and identify areas for improvement.
Potential Downsides
While competitive intelligence offers many advantages, there are potential drawbacks:
-
Ethical & Legal Risks: Improperly gathering intelligence can result in legal issues.
-
Information Overload: Without proper analysis, large amounts of data can become overwhelming and unhelpful.
-
Reactive Strategies: Focusing too much on competitor actions can hinder innovation and lead to reactive strategies.
-
Data Accuracy: Verifying the accuracy of some intelligence can be difficult.
-
Resource Intensive: A robust competitive intelligence program demands significant resources.
You might find this helpful: Our guide on top stock market analysis techniques offers additional insights on market analysis.
History and Development
The field of competitive intelligence gained traction through the work of pioneers like Leonard Fuld and organizations like the Society of Competitive Intelligence Professionals (SCIP). Corporate intelligence units in companies like Procter & Gamble and IBM, along with Michael Porter's competitive strategy frameworks, further emphasized its importance.
Tips for Effective Competitive Intelligence Gathering
Here are some tips for effective competitive intelligence gathering:
-
Establish Ethical Guidelines: Set clear rules for your intelligence gathering activities.
-
Focus on Patterns: Look for trends and patterns instead of isolated data points.
-
Systematic Processes: Create structured processes for information collection, analysis, and sharing.
-
Employee Training: Teach employees to identify and report valuable competitive insights.
-
Specialized Software: Use software tools to organize, analyze, and visualize competitive data.
Competitive Intelligence Gathering is a valuable tool for traders and investors. By systematically gathering and analyzing information, you can improve investment decisions, reduce risks, and uncover hidden opportunities. It offers a significant advantage in today’s competitive markets.
5. Social Listening and Digital Monitoring
Social Listening and Digital Monitoring is an essential market scanning technique. It involves tracking online conversations, sentiment, and trends across digital channels. These include social media platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram, review sites like Yelp and TripAdvisor, forums such as Reddit and specialized industry forums, plus news websites and blogs. This technique helps organizations, particularly those in finance, understand customer perceptions, identify emerging issues, track brand reputation, and spot market opportunities. By analyzing these digital signals, companies can detect shifts in consumer preferences and behavior, often before they show up in traditional market research. This offers a significant advantage.
Why Social Listening Matters for Financial Professionals
For traders, analysts, and investors, understanding market sentiment is crucial. Social listening provides insights into the collective consciousness surrounding specific assets, industries, or even macroeconomic trends. Recognizing early warning signs of changing sentiment, identifying emerging investment themes, and gauging the impact of news events on public perception can inform trading strategies and investment decisions.
Features and Benefits of Social Listening
- Real-time monitoring: Track conversations and news as they unfold, allowing for quick reactions to market shifts.
- Sentiment analysis: Measure the overall positive, negative, or neutral sentiment surrounding specific stocks, sectors, or economic indicators.
- Influencer identification: Identify key individuals who drive online conversations and shape public opinion within financial markets.
- Trend identification: Spot emerging trends, hashtags, and keywords to uncover potential investment opportunities or risks.
- Competitive intelligence: Analyze discussions about competitors to understand their strategies and market positioning.
Pros of Social Listening
- Unfiltered consumer feedback: Access direct, unfiltered opinions and reactions to market events.
- Early trend detection: Identify emerging trends before they become widespread, enabling proactive investment strategies.
- Cost-effectiveness: Compared to traditional market research, social listening offers a more affordable way to gain valuable insights.
- Rapid response: Quickly react to market events and adjust strategies based on real-time data.
Cons of Social Listening
- Sample bias: Data primarily reflects the views of digitally active individuals, which might not represent the entire market.
- Data overload: The substantial amount of data requires specialized tools and expertise for effective filtering and analysis.
- Privacy concerns: Ethical considerations regarding data collection and privacy need to be addressed.
- Sentiment analysis challenges: Accurately interpreting sarcasm, humor, and context can be difficult for automated sentiment analysis tools.
Real-World Examples of Social Listening in Finance
- Hedge funds using social sentiment to predict stock price movements: Analyzing online discussions about specific companies helps anticipate shifts in investor sentiment and potentially predict short-term price changes.
- Investment banks tracking social media during IPOs: Monitoring social media buzz around upcoming IPOs can help gauge investor interest and refine pricing strategies.
- Retail investors using social platforms for trading ideas: Online communities and forums provide valuable insights into crowd-sourced sentiment and potential investment opportunities.
Tips for Implementing Social Listening
- Define clear objectives: Determine the specific information you need. Are you tracking specific stocks, sectors, or broader market trends?
- Choose the right tools: Social listening platforms like Brandwatch and Sprinklr offer specialized features for financial market analysis. Explore options and select tools that fit your needs and budget. Hootsuite is also a popular social media management platform.
- Combine automated tools with human analysis: While automated tools are essential for data collection and processing, human analysis is crucial for interpreting context, nuances, and sarcasm.
- Focus on actionable insights: Concentrate on data that can directly inform your trading or investment decisions.
- Monitor both branded and unbranded conversations: Track mentions of specific companies as well as general industry discussions to gain a comprehensive market view.
Social Listening and Digital Monitoring, popularized by platforms like Brandwatch and Sprinklr, along with thought leaders like Seth Godin, leverages the power of online conversations to understand consumer behavior. For financial professionals, integrating social listening into your market scanning toolkit offers a crucial advantage. It enables you to anticipate market movements, identify emerging opportunities, and make more informed decisions in today's fast-paced financial landscape.
6. Scenario Planning
Scenario planning is a powerful market scanning technique, especially useful for professional traders, analysts, and financial institutions navigating uncertain markets. Unlike traditional forecasting, which tries to predict a single future outcome, scenario planning explores multiple plausible futures. This prepares you for a range of potential market conditions. This proactive approach allows for more robust strategies and quicker adaptation to market shifts.
Instead of asking "what will happen?", scenario planning asks "what could happen?" It involves identifying key uncertainties and driving forces in the market. These might include interest rate fluctuations, regulatory changes, technological disruptions, or geopolitical events. Scenario planning then constructs narratives around how these factors might interact to shape different future scenarios.
How Scenario Planning Works:
The scenario planning process typically involves these five key steps:
-
Identifying Key Uncertainties: Pinpointing the most critical factors with the greatest potential impact on the market. For a trader, this could be the direction of interest rates, the outcome of a trade war, or the adoption rate of a new technology.
-
Developing Plausible Scenarios: Crafting detailed narratives around a few distinct, yet plausible, future states. These narratives should be internally consistent and explore the potential consequences of different combinations of uncertainties. For example, a trader might develop scenarios around a "bull market with high inflation," a "bear market with low inflation," and a "stagflationary environment."
-
Analyzing Implications: Examining how each scenario would impact investment strategies, portfolio performance, and overall market dynamics. This involves considering the potential risks and opportunities presented by each scenario.
-
Developing Contingency Plans: Formulating specific actions and adjustments to be taken if indicators suggest a particular scenario is unfolding. This proactive approach enables faster and more effective responses to market changes.
-
Identifying Early Warning Indicators: Defining specific, measurable indicators that would signal the emergence of a particular scenario. These indicators serve as triggers for implementing pre-determined contingency plans.
Real-World Examples:
Scenario planning has proven effective across diverse sectors:
-
Royal Dutch Shell: Shell used scenario planning to anticipate and navigate the oil crises of the 1970s. This foresight gave them a significant advantage.
-
Financial Institutions: Banks and investment firms use scenario planning to assess risks and develop strategies for different interest rate environments, regulatory changes, and economic downturns. Stress testing is a specific application of scenario planning.
-
Trading Strategies: Traders use scenario planning to develop robust strategies that perform well across various market conditions, rather than relying on a single market prediction. For example, preparing for a sudden market crash or an unexpected surge in volatility can help mitigate losses and capitalize on opportunities.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Improved Decision-Making: Prepares you for multiple potential outcomes.
- Enhanced Agility: Develops adaptive capacity.
- Early Warning System: Identifies indicators that signal market shifts.
- Overcoming Biases: Challenges assumptions and reduces the influence of cognitive biases.
Cons:
- Resource Intensive: Developing robust scenarios requires time and effort.
- Potential for Dismissal: Some may view scenario planning as impractical.
- Implementation Challenges: Translating scenarios into concrete action plans can be difficult.
Tips for Implementation:
- Focus: Concentrate on a manageable number of scenarios (3-5).
- Plausibility: Ensure scenarios are plausible, distinctive, and challenging.
- Narratives: Develop engaging narratives to aid communication.
- Indicators: Identify specific, measurable indicators for each scenario.
- Review: Revisit and update scenarios regularly.
Popularized By:
Scenario planning gained prominence through the work of Pierre Wack and Peter Schwartz at Royal Dutch Shell, and organizations like the Global Business Network (GBN) and the Stanford Research Institute (SRI International).
Scenario planning's strength lies in preparing for uncertainty. By embracing a multi-future perspective, traders and financial professionals can develop more robust strategies, enhance their adaptability, and improve their decision-making. It's a valuable tool for moving beyond simplistic predictions and embracing the complexities of the financial world.
7. Customer Journey Mapping
Customer Journey Mapping is a powerful market scanning technique. It lets you visualize the complete experience a customer has with your product, service, or brand. Unlike traditional market research, which often focuses on isolated data points, journey mapping provides a holistic view of the customer. This includes their interactions, emotions, and pain points across all touchpoints. These touchpoints range from initial awareness to post-purchase engagement. For market analysts, traders, and investors, understanding the customer journey can reveal crucial insights. These insights relate to market opportunities, competitive advantages, and potential investment risks.
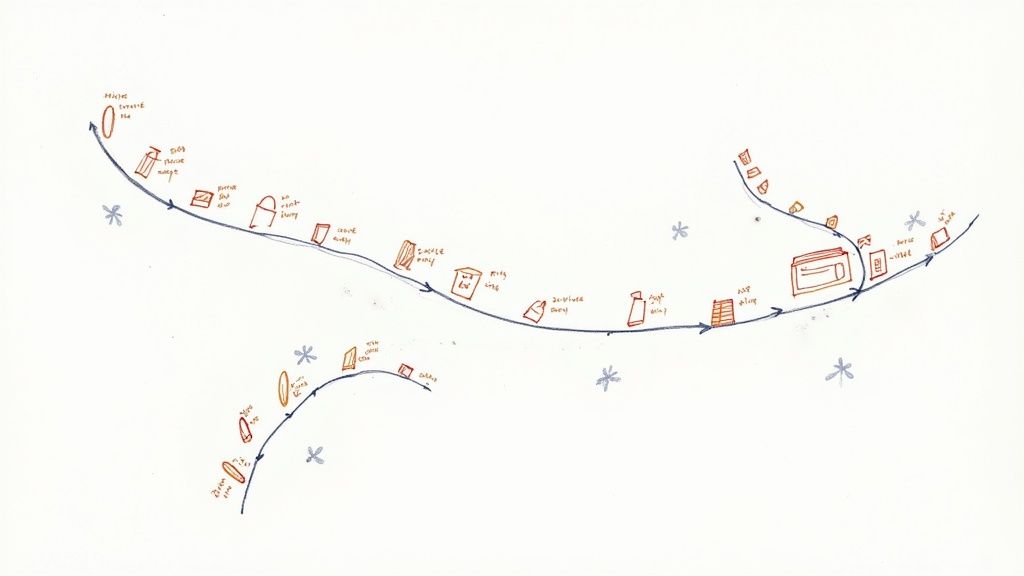
This visual representation typically unfolds chronologically. It outlines the stages a customer goes through. This includes their thoughts, emotions, and actions at each step. It incorporates multiple channels – online, offline, and mobile. It also includes various interaction types. This offers a comprehensive understanding of the overall customer experience. The method can even incorporate quantitative metrics. These include time spent on a task, costs incurred, and conversion rates. It can also include qualitative insights such as customer satisfaction scores and feedback.
Features and Benefits
-
Visual Clarity: The visual format of a customer journey map makes it easy to identify bottlenecks, pain points, and opportunities for improvement.
-
Customer-Centricity: It shifts the focus from internal processes to the customer's perspective. This provides a deeper understanding of their needs and motivations.
-
Actionable Insights: By pinpointing specific areas for improvement, journey mapping helps prioritize investments and resource allocation for maximum impact.
-
Cross-Functional Alignment: It breaks down organizational silos by providing a shared understanding of the customer experience across different departments.
-
Predictive Power: By understanding customer behavior patterns, businesses can anticipate future needs and proactively address potential issues. This is valuable for investors assessing the long-term viability of a company.
Real-World Examples
-
Amazon's One-Click Ordering: Amazon identified the friction point of multiple checkout steps. They introduced one-click ordering, changing the online shopping experience. This innovation directly impacted their market share and stock value.
-
IKEA's Store Layout: IKEA used journey mapping to understand how customers navigate their stores. This led to a redesigned layout that optimized the shopping flow and increased sales.
-
Capital One's Digital Banking: Capital One used journey mapping to enhance its digital banking platform. They addressed user pain points and improved customer satisfaction.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Provides a customer-centric view of market opportunities.
- Identifies gaps and pain points that represent market openings.
- Helps prioritize investments based on customer impact.
- Breaks down organizational silos around customer experience.
- Makes abstract customer needs concrete and actionable.
Cons:
- Can oversimplify diverse customer experiences into a single journey.
- Resource intensive to create and maintain comprehensively.
- May focus on existing customers at the expense of non-customers.
- Difficult to capture emotional elements accurately.
- Risk of confirmation bias in journey construction.
Tips for Implementation
-
Involve Real Customers: Gather feedback directly from customers through interviews, surveys, and focus groups to ensure accuracy and relevance.
-
Create Persona-Specific Journeys: Develop journeys for different customer segments to address their unique needs and behaviors. For traders, this could mean mapping journeys for different investor profiles.
-
Incorporate Quantitative Data: Use data analytics to track customer behavior and measure the impact of changes made based on journey mapping insights. This is crucial for investors evaluating a company’s performance.
-
Focus on Emotions and Motivations: Understand the underlying reasons behind customer actions to gain deeper insights.
-
Update Journey Maps Regularly: Customer behavior is constantly evolving, so it's important to keep your journey maps up-to-date.
Evolution and Popularization
Customer Journey Mapping has roots in service design and user experience (UX) research. Organizations like IDEO, the Service Design Network, and the Nielsen Norman Group have helped popularize and refine the technique. Articles on customer experience from Harvard Business Review (HBR) further cemented its place in business strategy. Today, it's a crucial tool for understanding customer behavior and driving business growth. It is an essential technique for market analysis and investment decisions. By revealing the "why" behind market trends, customer journey mapping gives analysts and investors a significant edge. This edge helps them understand market dynamics and predict future performance.
8. Trend Analysis and Forecasting
Trend Analysis and Forecasting is a crucial market scanning technique for anyone involved in financial markets, from seasoned traders to individual investors. It involves identifying, monitoring, and projecting patterns and trends that can influence markets, consumer behavior, and ultimately, business performance. This technique combines quantitative methods like statistical analysis and time series forecasting with qualitative approaches like expert opinions and trend watching to anticipate market developments and support data-driven strategic decisions.
By understanding emerging trends, organizations can detect shifts in markets before they become widespread, gaining a significant competitive advantage.
This technique relies on combining historical data analysis with forward-looking projections. By examining multiple timeframes (short, medium, and long-term), analysts can differentiate between short-lived fads, sustainable trends, and impactful megatrends.
Often, these trends are categorized by their potential impact and probability, allowing for a prioritized approach to resource allocation and strategic planning.
Examples of Trend Analysis Success
- Whole Foods: Capitalized on the organic food trend early on, establishing themselves as a market leader.
- Netflix: Accurately forecasted the rise of streaming video, propelling them to the forefront of the entertainment industry.
- Target: Maintains a dedicated trend department, predicting fashion and home design trends, consistently positioning them to meet evolving consumer demands.
- Automotive Industry: Utilizes trend analysis and forecasting to project electric vehicle adoption and adapt production strategies.
Effective trend analysis and forecasting incorporates both quantitative and qualitative methodologies, examining multiple timeframes, and distinguishing between fads, trends, and megatrends. It often involves categorizing trends by their potential impact and probability.
This approach offers several key benefits:
- Early warning of market shifts
- Anticipating changing customer needs
- Evidence-based strategic planning
- Identifying opportunities for product development and innovation
- Reducing the risk of being unprepared for market changes
Limitations of Trend Analysis
Like any analytical technique, trend analysis has its limitations. Historical trends may not always accurately predict future developments. There’s also a risk of confirmation bias influencing trend identification, where analysts may favor data that supports pre-existing beliefs. Determining which trends will have a lasting impact can be challenging, and disruptive innovations that don't follow established patterns can be easily missed. Furthermore, trend analysis requires continuous updating as market conditions change.
For more detailed information, you might find this resource helpful: How to Identify Market Trends: A Complete Guide to Finding Hidden Opportunities.
Tips for Effective Trend Analysis
- Distinguish between meaningful patterns (signals) and random fluctuations (noise).
- Utilize multiple forecasting methods and compare results.
- Develop trend tracking dashboards with key indicators.
- Assemble cross-functional trend teams with diverse perspectives.
- Meticulously document the assumptions underlying your trend projections for later validation.
The work of trend forecasters like Faith Popcorn (BrainReserve), Trendwatching.com, The Future Laboratory, and WGSN (trend forecasting service) has popularized and refined these techniques.
Trend Analysis and Forecasting is an invaluable tool for investors and traders. It provides foresight in the fast-paced world of finance. Understanding emerging trends is essential for survival and success. By proactively identifying and analyzing potential market shifts, you can make informed decisions, optimize your strategies, and gain a competitive edge.
Market Scanning Techniques: 8-Point Comparison Guide
| Technique | Implementation Complexity (🔄) | Resource Requirements (⚡) | Expected Outcomes (📊) | Ideal Use Cases (💡) | Key Advantages (⭐) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PESTEL Analysis | High | High | Comprehensive insights into macro-environmental factors | Strategic planning and risk management in varied markets | Holistic view with long-term strategic focus |
| Porter's Five Forces Analysis | Medium | Medium | Deep understanding of competitive dynamics and industry forces | Competitive analysis and market entry decisions | Clear analysis of rivalry and profit potential |
| Technology Scouting | High | High | Early warning on disruptive and emerging technologies | R&D, innovation management, and technology adoption | Proactive identification leading to first-mover advantage |
| Competitive Intelligence Gathering | Medium | Medium | Actionable insights into competitors’ strategies and market gaps | Benchmarking, strategic market positioning, and pricing | Reduces surprises with ongoing market and competitor monitoring |
| Social Listening and Digital Monitoring | Medium | Medium | Real-time consumer sentiment and trend detection | Brand reputation management and agile digital marketing | Rapid feedback and cost-effective market pulse detection |
| Scenario Planning | High | High | Multiple plausible future scenarios and contingency strategies | Strategic planning in uncertain and volatile environments | Enhances organizational agility and preparedness |
| Customer Journey Mapping | Medium | Medium | Clear visualization of customer experiences and pain points | Improving customer experience and service design | Breaks down silos and translates experiences into actionable insights |
| Trend Analysis and Forecasting | Medium | Medium | Early detection and projection of market trends | Evidence-based planning and market forecasting | Proactive risk reduction through systematic trend tracking |
Sharpening Your Competitive Edge
Mastering market scanning is crucial for success in the dynamic financial world. By effectively using techniques like PESTEL analysis, Porter's Five Forces, technology scouting, competitive intelligence gathering, social listening, scenario planning, customer journey mapping, and trend analysis, you gain a comprehensive understanding of the market. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions, anticipate market shifts, and proactively adapt your strategies. These techniques are not one-time activities; they should be integrated into your ongoing workflow.
Integrating market scanning into your routine allows you to constantly refine your approach and stay ahead of the competition. Think of it as a continuous feedback loop, constantly providing valuable insights.
Implementing Effective Market Scanning
Applying these concepts requires a structured and iterative approach.
- Define Objectives: Start by clearly defining your objectives and the scope of your analysis. What specific information are you looking for? What are your goals?
- Gather and Analyze Data: Systematically gather and analyze data using the appropriate techniques. Each method offers unique perspectives, allowing you to build a more complete picture.
- Review and Refine: Regularly review and refine your findings, adapting your strategies as needed based on the evolving market. This consistent evaluation ensures your strategies remain relevant and effective.
This continuous learning process is vital for staying ahead of the curve and adapting to new market realities.
Staying Ahead of the Curve
The financial markets are in constant flux, influenced by emerging technologies, regulatory changes, and shifting investor sentiment. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and alternative data are transforming how we analyze and interpret market data. Staying informed about these trends and future developments is paramount for maintaining your competitive edge. Embrace continuous learning and explore new tools and techniques to enhance your market scanning capabilities. This proactive approach will allow you to identify opportunities and mitigate risks.
Key Takeaways
- Proactive Adaptation: Market scanning enables you to anticipate and adapt to market changes, minimizing risks and maximizing opportunities. Being prepared allows you to capitalize on emerging trends.
- Informed Decision-Making: Leverage data-driven insights to make informed investment decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics. Solid data is the foundation of successful strategies.
- Competitive Advantage: Stay ahead of the competition by identifying emerging trends, understanding competitor strategies, and adapting quickly to market shifts. Agility is key in today's fast-paced markets.
- Continuous Learning: Embrace ongoing learning and adapt your strategies based on the evolving market landscape and technological advancements. Never stop learning and refining your approach.
Elevate Your Market Scanning with ChartsWatcher
To truly elevate your market scanning efforts and capitalize on these powerful techniques, consider ChartsWatcher, a sophisticated stock market scanning software. ChartsWatcher empowers you to efficiently track and analyze market movements with precision. Customize your dashboards, set up alerts, backtest your strategies, and access real-time data all within a dynamic and intuitive interface. From customizable screen configurations to advanced filtering options, ChartsWatcher provides the tools you need to gain a decisive edge in the market. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or just starting out, ChartsWatcher offers flexible pricing plans to suit your needs, from a free basic package to a comprehensive Pro Plan. Start maximizing your market insights and refine your trading strategies today with ChartsWatcher.

