Master Backtesting Trading Strategies for Better Results
The Power Behind Backtesting Trading Strategies
Deploying capital without understanding potential outcomes is like gambling. That's where backtesting trading strategies becomes crucial. Backtesting simulates strategies against historical market data, offering a glimpse into past performance. This transforms historical behavior into predictive insights, separating true edge from noise.
Understanding the Core Principles
Predicting the weather without past patterns would be impossible. Similarly, successful trading relies on understanding historical market patterns. Backtesting allows traders to analyze these patterns systematically. It’s the difference between casually reviewing charts and rigorous testing.
This systematic approach helps evaluate potential profitability. A day trader might backtest based on candlestick patterns, while a swing trader might use moving averages. Backtesting identifies approaches with the highest probability of success under specific market conditions.
From Intuition to Validation
Even seasoned discretionary traders, relying on experience and intuition, increasingly use backtesting. Why? It validates intuitions, providing an objective measure of effectiveness. This builds confidence before risking real capital, distinguishing amateur from professional approaches.
Backtesting also quantifies risk using metrics like maximum drawdown and win rates. A strategy tested over 10 years (2010–2020) on S&P 500 data might reveal a 25% maximum drawdown and a 55% win rate, exposing vulnerabilities during the 2020 selloff. This helps traders assess risk-reward ratios. Even high win rates can fail if drawdowns are too high. Hedge funds often require multi-decade backtests, rejecting strategies with annualized returns below 15% or Sharpe ratios under 1.5, filtering out unviable approaches. Learn more about analyzing backtesting data here: Backtesting Investment Strategies with Historical Data: A Guide to Smarter Investing

The Benefits of Backtesting Trading Strategies
Understanding the past informs future decisions. This leads to:
- Reduced Risk: Backtesting identifies potentially disastrous strategies.
- Increased Profitability: Identifying and refining successful strategies enhances returns.
- Improved Confidence: Backtested strategies instill greater decision-making confidence.
- Disciplined Approach: Backtesting fosters a systematic, less emotional approach.
Backtesting isn't just beneficial; it's foundational for successful, sustainable trading. It provides a framework to evaluate and refine your approach, leading to better decisions and results.
Building Your Backtesting Ecosystem
A reliable backtesting ecosystem is the foundation of any successful trading strategy. It's not just about the software; it's about creating a robust environment that closely mirrors real-world market conditions. This involves carefully choosing your data sources, selecting the right software, and, crucially, accounting for trading costs. Let's explore each element of this crucial ecosystem.
Building a robust backtesting ecosystem starts with the data that fuels it.
The Importance of Quality Data
Just like a chef needs the freshest ingredients, effective backtesting relies on high-quality market data. Inaccurate or incomplete data will skew your results and could lead to poor trading decisions. Successful quantitative traders understand this and prioritize reliable data sources. This often means investing in premium data providers known for their accuracy and comprehensive historical coverage, rather than solely relying on free resources. This commitment to data quality is often what distinguishes profitable strategies from the rest.
Quality data is only as good as the tools used to analyze it.
Selecting The Right Software Tools
The software you choose plays a vital role in your backtesting ecosystem. The right tools allow you to accurately simulate your trading strategies and effectively interpret the results. A wide range of solutions is available, from free, open-source platforms to sophisticated, commercial software packages. The best choice depends on your individual trading style, technical expertise, and budget. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on How to master backtesting.
For beginners, a user-friendly platform with a visual interface is often the best starting point. For experienced programmers, platforms like Python with scripting capabilities and API access offer greater flexibility.
To help you choose, let's look at some popular backtesting software options:
To illustrate the different software choices available and their suitability for various trader levels, let's examine a comparison table. The following table, "Backtesting Software Comparison," highlights key features, price ranges, and the asset classes each platform supports. It also considers the level of programming knowledge required.
| Platform | Price Range | Asset Classes | Programming Required | Suitable For | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Google Sheets / Microsoft Excel | Free / Paid | Stocks, Futures, Options, Forex | Basic | Beginners, simple strategies | Basic calculations, charting |
| TradingView | Free / Paid | Stocks, Futures, Options, Forex, Crypto | Basic / Advanced (Pine Script) | Visual learners, chart analysis | Built-in charting, some scripting, community features |
| Python Libraries (e.g., Backtrader, Zipline) | Free | Stocks, Futures, Options, Forex, Crypto | Advanced | Programmers, complex strategies | Flexibility, extensive libraries |
| Bloomberg Terminal | Paid (Expensive) | All Asset Classes | Varies | Professional Traders, Institutions | Advanced analytics, real-time data, news and research |
| MetaTrader | Free / Paid | Forex, CFDs | Basic / Advanced (MQL) | Forex Traders | Automated trading, charting, technical analysis |
Key takeaways from the table: free options like spreadsheets and TradingView are excellent starting points, while Python offers more advanced capabilities for programmers. Dedicated platforms like Bloomberg and MetaTrader cater to specific needs and experience levels.
Don't forget: choosing software is a crucial part of building your backtesting ecosystem, and the ideal tool depends on your individual needs and preferences.
Even with the perfect software and data, it's important to be realistic.
Accounting For Real-World Factors
Experienced traders know that simulated profits don't always translate to real-world gains. Factors like slippage (the difference between the expected price and the actual execution price), commissions, and market liquidity can significantly impact your bottom line. It's crucial to incorporate these elements into your backtesting process. Advanced backtesting software allows you to simulate slippage and commissions realistically. Ignoring these seemingly small details can create overly optimistic backtest results and ultimately lead to disappointment when you start live trading.
Realism in backtesting is key to avoiding surprises in live trading.
Visualizing Performance: Key Metrics in Action
The following data chart illustrates how incorporating real-world costs can impact the performance of different trading strategies. It shows the theoretical performance versus the performance after accounting for slippage and commissions.
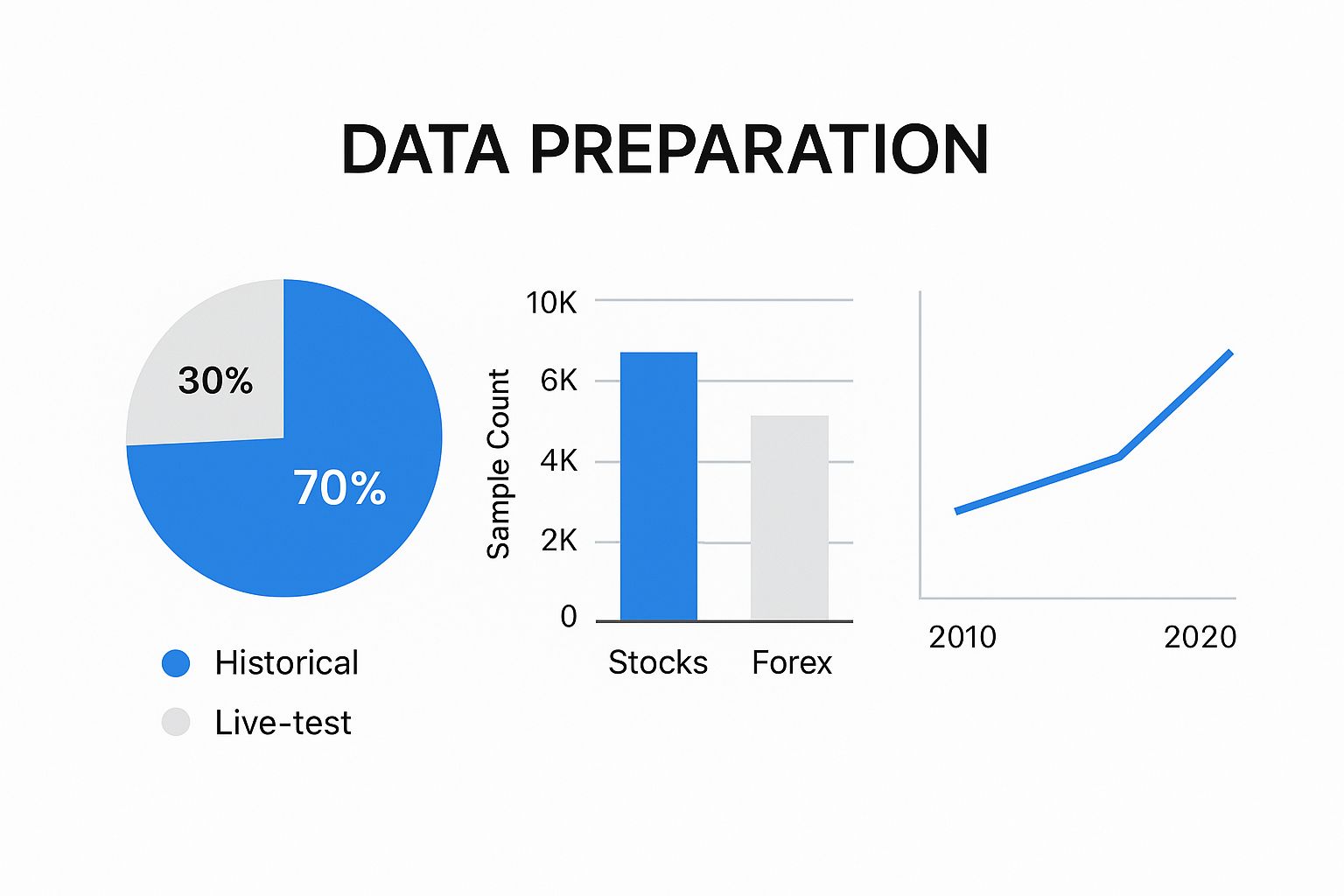
As shown in the data chart, Strategy A initially appears promising but suffers greatly when realistic costs are applied. Strategy B shows consistent, albeit moderate returns, demonstrating better cost management. Strategy C, while having lower theoretical returns, maintains its performance even after costs are factored in, showcasing its robustness.
This data chart emphasizes the importance of incorporating real-world costs into your backtesting process. A strategy that looks fantastic on paper can underperform dramatically in live trading due to the impact of these costs. Building a robust backtesting ecosystem requires recognizing these nuances and selecting tools that accurately reflect market conditions. This leads to better assessment of strategy viability and more informed trading decisions.
Beyond Profit: Performance Metrics That Actually Matter

While profitability is the ultimate goal, focusing solely on potential profits when backtesting trading strategies can be misleading. A deeper understanding of performance metrics is crucial. Experienced fund managers emphasize the need for a comprehensive performance dashboard that goes beyond simple profit. They understand the importance of examining metrics that truly reflect a strategy’s robustness and sustainability.
Maximum Drawdown: A Key Indicator of Risk
A frequently overlooked, yet critical, metric is the maximum drawdown. This represents the peak-to-trough decline during a specific period, revealing the largest loss a strategy has encountered. A strategy might show high returns, but also a substantial drawdown, indicating significant risk.
For example, a 50% drawdown could overshadow impressive returns. This information is vital for assessing whether potential rewards justify the inherent risks. Professional traders prioritize maximum drawdown as a key indicator of a strategy’s viability.
Risk-Adjusted Returns: The Sharpe and Sortino Ratios
Traders use risk-adjusted return metrics to evaluate the true effectiveness of their backtested trading strategies. The Sharpe Ratio compares excess returns to their volatility, helping to identify consistent, low-volatility performers.
However, the Sharpe Ratio penalizes both positive and negative volatility. The Sortino Ratio addresses this by focusing solely on downside volatility. A strategy with frequent small gains and occasional large losses might have a high Sharpe Ratio but a low Sortino Ratio, revealing hidden risks. This distinction is crucial for selecting strategies built to withstand market downturns. For a deeper dive into performance metrics, check out this helpful article: How to master trading performance metrics.
Demystifying Complex Calculations
While these metrics may seem complex, they directly inform practical trading decisions. The Sharpe and Sortino ratios help traders choose consistent performers. Maximum drawdown informs risk management protocols. Understanding these metrics enables traders to build a robust, realistic evaluation framework.
From Theory to Practice: Real-World Examples
Real-world examples best illustrate the importance of these metrics. Imagine two hypothetical strategies backtested over the same period. Strategy A yields a 100% return, while Strategy B yields a 50% return. However, Strategy A experienced a 70% maximum drawdown, compared to Strategy B's 10% drawdown. This demonstrates how a seemingly less profitable strategy (B) can be significantly more robust and sustainable over time.
Building a Comprehensive Evaluation Framework
Backtesting isn't just about finding profitable strategies; it's about finding sustainable ones. This means looking beyond simple profit calculations and incorporating a broader range of performance metrics. By understanding and using metrics like maximum drawdown, the Sharpe Ratio, and the Sortino Ratio, traders can build a more comprehensive evaluation framework, leading to better trading decisions and more consistent returns.
Metrics Beyond the Basics: Exploring Further
Analyzing backtesting data goes beyond Sharpe and Sortino ratios. Other important metrics include:
-
Win Rate: The percentage of winning trades. A consistently high win rate, even with smaller average wins, can contribute significantly to long-term profitability.
-
Profit Factor: The ratio of gross profit to gross loss. A profit factor consistently above 1 indicates that winning trades outweigh losing trades in monetary value.
-
Calmar Ratio: This measures the annualized return relative to the maximum drawdown, emphasizing strategies that achieve high returns while minimizing risk.
By combining these metrics with Sharpe and Sortino ratios, traders develop a holistic view of a strategy’s performance. This multifaceted approach is essential for identifying robust strategies that can withstand real-world market conditions.
Pressure-Testing Your Strategy Across Market Conditions
Backtesting trading strategies against historical data is essential, but it's only the first step. Markets are dynamic, constantly shifting. A strategy that excels in a trending market might struggle during periods of consolidation. This is why stress testing is crucial. It helps uncover hidden vulnerabilities and separates robust, long-term strategies from those destined to fail when market dynamics change.
Categorizing Historical Data into Market Regimes
Effective stress testing requires categorizing historical data into distinct market regimes. This goes beyond simple "bull" or "bear" labels, requiring a more nuanced approach:
- Trending Markets: Sustained upward or downward price movements, where trend-following strategies often perform well.
- Range-Bound Markets: Prices fluctuate within a defined range, favoring mean-reversion strategies.
- Crisis Periods: Extreme volatility and sharp declines, testing a strategy's resilience and risk management.
Segmenting data this way allows us to evaluate performance in each regime, revealing potential weaknesses specific to certain market environments.
Identifying Vulnerabilities During Market Transitions
Many strategies falter not during stable regimes, but during market transitions. A trend-following strategy might experience losses as a trending market becomes range-bound. A mean-reversion strategy, optimized for quiet markets, can be caught off guard by a volatility spike. Testing performance between regimes is as important as testing within them.
The 2008 financial crisis provides a key example. Many trend-following systems reportedly returned 20-40% that year. However, strategies over-optimized for 2008 often underperformed in the subsequent low-volatility years (2013-2016). This illustrates the danger of overfitting to specific events. Effective backtesting necessitates analysis across multiple economic cycles, with institutional traders often requiring 500-1,000 simulated trades. Learn more about backtesting pitfalls here: The Ultimate Guide to Backtesting.
Utilizing Scenario Analysis and Monte Carlo Simulations
Past performance offers valuable insights, but it can't predict the future. Scenario analysis addresses this by creating "what-if" scenarios. Key parameters like volatility or interest rates are adjusted to observe how the strategy performs under these altered conditions. Simulating a sudden interest rate hike or a flash crash helps evaluate resilience to unexpected events.
Monte Carlo simulations expand on scenario analysis. Thousands of simulations are run with randomly varied inputs, extending testing beyond historical data. This provides a more robust understanding of probabilistic behavior and the potential range of outcomes.
Building a Framework for Robust Backtesting
A robust backtesting framework should incorporate:
- Regime Identification: Categorize historical data into distinct market regimes.
- Transition Analysis: Evaluate performance during shifts between regimes.
- Scenario Analysis: Simulate "what-if" scenarios, including crisis events.
- Monte Carlo Simulations: Run thousands of simulations with randomized inputs.
These elements provide a comprehensive and realistic assessment of a strategy's strengths and weaknesses, leading to more informed trading decisions and improved long-term performance. Platforms like ChartsWatcher can greatly assist in this process, offering customizable dashboards and advanced filtering options.
Avoiding the Backtest Traps That Sink Trading Accounts
Even with a robust backtesting system, deceptive practices can lead to unrealistic outcomes. Many traders, even seasoned professionals, can fall victim to biases that skew testing data. This creates backtests that appear incredibly promising, but ultimately fail to deliver in live trading. This section explores these common pitfalls and how to navigate them effectively.
Look-Ahead Bias: Accidentally Using Future Information
One of the most subtle yet dangerous traps is look-ahead bias. This happens when your backtest unknowingly uses information that wouldn't have been accessible at the time a trade should have been made.
For example, basing intraday trading decisions on end-of-day prices introduces look-ahead bias. You wouldn't have the closing price at the start of the trading day. This seemingly small error can significantly inflate backtested performance, giving you a false sense of security.
Survivorship Bias: Ignoring Delisted Stocks
Survivorship bias is another frequent issue, especially when backtesting stock strategies. Many databases only contain currently listed stocks, excluding companies that went bankrupt or were delisted.
This omission paints a distorted picture of historical performance. Your backtest might overlook critical periods of market downturn where many companies failed, leading to an overestimation of potential returns.
Psychological Biases: Confirmation and Recency
Even backtesting can be influenced by psychological biases. Confirmation bias can lead traders to focus on data supporting their pre-existing beliefs, potentially ignoring flaws in their strategies.
Recency bias overemphasizes recent market behavior. A strategy optimized for the last few months could underperform when market conditions shift. These biases often result in over-optimized, fragile strategies that collapse under real-world trading pressures.
Identifying Red Flags and Maintaining Objectivity
Spotting red flags is paramount. Unusually high returns with minimal drawdowns warrant further investigation. Compare your results to a relevant benchmark. If your backtest consistently and significantly beats the market, scrutinize it for hidden biases.
Maintain an objective perspective. Approach your backtest like a scientific experiment, actively searching for evidence that might invalidate your strategy, not just confirm it.
Institutional Frameworks: Systematic Bias Elimination
Institutional trading desks utilize rigorous frameworks to mitigate these biases:
- Data Integrity Checks: Verify data accuracy and completeness, especially for historical market events.
- Out-of-Sample Testing: Test the strategy on data separate from the development set to ensure robustness.
- Blind Testing: Conduct backtests without knowing the underlying market conditions to minimize confirmation bias.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Evaluate the impact of changes in crucial parameters like slippage and commissions on overall results.
These frameworks encourage objectivity and help ensure that backtested performance realistically reflects potential real-world outcomes. By adopting these best practices, individual traders can drastically enhance the reliability of their backtests and avoid costly mistakes from overly optimistic simulations. This allows for a smoother transition from simulated trading to live markets, bridging the gap between backtested results and actual trading performance.
Tailoring Your Approach: Asset-Specific Backtesting
Backtesting trading strategies isn't a one-size-fits-all endeavor. Every asset class, from stocks and options to futures, forex, and cryptocurrency, presents its own unique set of characteristics and challenges. This means adapting your backtesting methodology to account for these nuances is crucial for reliable results.
Understanding Asset-Specific Dynamics
Why is a tailored approach so important? Consider liquidity modeling. It's paramount when backtesting options strategies due to the impact of bid-ask spreads and option Greeks. However, liquidity plays a less significant role in forex backtesting where high trading volume usually results in tight spreads.
Cryptocurrency backtesting adds another layer of complexity. The decentralized nature of these markets, with varying exchange-specific behaviors and regulations, demands close attention to data integrity and consistency. For instance, a strategy based on arbitrage between exchanges might yield vastly different results depending on which exchanges are included in your backtest.
Futures contracts, with their set expiry dates, require careful management of rollovers. Overlooking rollovers can skew backtest results by failing to account for transaction costs and potential slippage during contract transitions.
Foreign exchange strategies, in particular, benefit from backtesting due to the 24-hour market dynamics. A EUR/USD mean-reversion strategy tested across 15 years (2005–2020) might show impressive 60%+ win rates during range-bound periods but falter during major events like the 2015 Swiss Franc unpegging, where stop-loss orders might not execute. Stress tests like these are critical, as forex markets typically experience 5–10 major volatility spikes per decade. Modern backtesting platforms, like ChartsWatcher, incorporate slippage models showing 0.5–1.5 pip execution gaps during high-impact news, prompting traders to factor in buffers for profit targets.
Key Considerations for Each Asset Class
To help you understand the key factors for different asset classes, the following table summarizes critical backtesting considerations. It highlights data requirements, specific challenges, recommended timeframes, and the most critical metrics to track for each.
Backtesting Considerations by Asset Class: Key factors and special considerations when backtesting different financial instruments
| Asset Class | Data Requirements | Specific Challenges | Recommended Timeframes | Critical Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stocks | Historical price and volume, fundamental data | Survivorship bias, dividends, stock splits | Long-term (5+ years) | Sharpe Ratio, Maximum Drawdown |
| Options | Option chain data, implied volatility | Liquidity modeling, Greek sensitivities | Short to medium-term | Implied Volatility Crush, Theta Decay |
| Futures | Continuous contract data, rollover adjustments | Rollover costs, contract expirations | Medium-term | Contango/Backwardation, Open Interest |
| Forex | Tick data, economic calendar | Slippage during news events, 24/7 market | Short to medium-term | Profit Factor, Win Rate |
| Cryptocurrency | Exchange-specific data, order book information | Exchange inconsistencies, regulatory changes | Varies | Transaction Fees, Order Book Depth |
As this table illustrates, backtesting requires careful consideration of various factors depending on the asset class being analyzed. Understanding these nuances is crucial for developing robust trading strategies.
Multi-Asset Backtesting and Portfolio Strategies
Beyond individual asset classes, backtesting becomes even more vital when managing multi-asset portfolios. Understanding correlation effects and managing risk across different markets is paramount. A portfolio backtest reveals how diversified assets interact under various market conditions, facilitating optimized asset allocation and risk mitigation strategies.
Tailoring Your Software and Metrics
The backtesting software you choose should also align with your target asset class. Some platforms specialize in specific markets, offering tailored tools and data. Key metrics also vary in importance depending on the asset class. While the Sharpe Ratio is widely used for stocks, the Profit Factor might be more relevant for forex.
Ultimately, successful backtesting depends on adapting your methods to the specific characteristics of each market. This tailored approach ensures more accurate results, improved risk management, and better trading performance. Platforms like ChartsWatcher, with their focus on real-time data and customization options, provide the tools needed for effective asset-specific backtesting.
Bridging the Gap: From Backtest to Live Trading
Backtesting trading strategies is essential, but the true measure of success lies in live market execution. Moving from simulated trades to real capital can be difficult, requiring both psychological and technical adjustments. This section explores the key steps to effectively implement your backtested strategies in the live market.
The Importance of Paper Trading
Before risking real money, paper trading offers a valuable testing ground. It simulates live trading with real-time market data, but without actual capital. This lets you experience the emotional and practical aspects of executing your strategy under market conditions. It's a risk-free environment to refine order entry, manage positions, and test your emotional discipline. Consider it a vital practice run before the real event.
Scaling Positions: A Gradual Approach
Even after successful paper trading, starting with small positions when transitioning to live trading is critical. This lets you validate your backtested results in real market conditions without taking on excessive risk. As your confidence and live performance align with your backtests, you can gradually increase your position size. This measured approach helps you adapt to unforeseen market nuances and refine your strategy while minimizing potential losses.
Tracking Divergence: Expected vs. Actual Results
Bridging the gap between backtesting and live trading requires carefully tracking the differences between expected and actual results. Establish a system to compare key metrics from your live trades against your backtests. These metrics might include win rate, average profit/loss, maximum drawdown, and the Sharpe ratio. Significant deviations warrant further investigation.
Troubleshooting Discrepancies: Identifying the Root Causes
If substantial discrepancies arise, investigate the underlying reasons. Is slippage higher than anticipated? Are your order entry methods causing delays? Are there market conditions not adequately reflected in your backtests? Addressing these issues will help refine your strategy and execution.
Implementing Circuit Breakers: Protecting Your Capital
For new strategies, consider using circuit breakers. These are predefined thresholds that automatically stop trading if losses exceed a certain limit. This protective measure helps control downside risk, especially when transitioning a strategy from backtesting to live trading. Think of them as a safety net for your trading system.
Objective Criteria: Knowing When to Abandon a Strategy
Define clear, objective criteria for continuing or abandoning a strategy based on live performance. This prevents emotional decisions and protects your capital. These criteria might involve a maximum acceptable drawdown, a minimum required Sharpe ratio, or a specific number of consecutive losses.
The Psychological Shift: Managing Emotions in Live Trading
The psychological aspect of live trading can often be more challenging than the technical side. Fear, greed, and impatience can lead to deviations from your plan. Maintaining discipline and objectivity is essential. A trading journal can help you document emotions and decisions, allowing you to identify and address psychological biases impacting your performance.
Successfully bridging the gap between backtesting and live trading requires more than just a profitable strategy. It requires discipline, adaptability, and a robust framework for monitoring and adapting to real-world market dynamics. By following a systematic approach, managing risk effectively, and maintaining psychological control, traders can transition their backtested strategies into consistent live market success.
Ready to enhance your trading with powerful, customizable dashboards and real-time alerts? Explore ChartsWatcher today and experience the difference.

